Policy
AML Regime
A legal/institutional tool to detect and prevent Money Laundering of criminal proceeds
AML Framework refers to a comprehensive system that encompasses legal and financial system, and international cooperation, as it is a legal and institutional tool that detects and prevents domestic and international illegal money laundering.
The basic idea of Money Laundering, in general, is to disguise the illicit source of money as if it is legitimate, though detailed definition might vary by countries and its law, and the area of research for scholars. Korea defines Money Laundering as “criminal acts of disguising the fact of acquisition and disposal of assets or concealing such assets, or disguising and concealing for the purpose of evading taxes”. (FTRA Article 2(5))
Financial Intellilgence Unit(FIU) is a central, unified government body that collects and analyzes ML-related STRs from financial institutions, and disseminates to LEAs.
-

Financial Institution (FIs)
-
KoFIU from Financial Institution (FIs)
Financial
Transaction
Reporting -

KoFIU
-
Law Enforcement Agencies (LEAs) from KoFIU
Information
Dissemination -

Law Enforcement Agencies (LEAs)
Korea Financial Intelligence Unit (KoFIU) has been established pursuant to the Financial Transaction Reports Act (FTRA). In November 2001, when established, the KoFIU was originally within the Ministry of Finance and Economy (MOFE), but as a result of a government reorganization in February 2008, it was transferred to the Financial Services Commission (FSC) and extended its area of work to Counter Proliferation Financing.
The KoFIU is staffed with AML/CFT experts from the FSC, the Ministry of Justice (MOJ), the National Police Agency (NPA), the National Tax Service (NTS), the Korea Customs Service (KCS), the Financial Supervisory Service (FSS), and other relevant law enforcement agencies. The KoFIU works as an institutional link between financial institutions and law enforcement agencies by receiving suspicious transaction reports (STRs)from reporting entities, analyzing the STRs, and disseminating them to law enforcement agencies for further action.
Four major AML/CFT legislation of Korea include: 1) the Financial Transaction Reports Act (FTRA), 2) Act on Special Cases Concerning the Prevention of Illegal Trafficking in Narcotics, 3) Act on Regulation and Punishment of Criminal Proceeds Concealment, and 4) Act on Prohibition against the Financing of Terrorism and Proliferation of Weapons of Mass Destruction. The Financial Transaction Reports Act serves as a legal ground of adopting Suspicious Transaction Report (STR), where transactions suspected to be involved in money laundering and tax evasion have to be reported to the head of FIU by financial institutions. FTRA allows foreign exchange of information as well, based on the principle of reciprocity. As of 22th December, 2008, financial institutions are required to report to FIU when identifies suspicious transaction. Secrecy of financial transaction is also covered by the Act. Yet, the Proceeds of Crime Act (POCA), criminalizes money laundering and provides for the confiscation of criminal proceeds. Under Article 3 of POCA, any person who disguises the acquisition or disposition of criminal proceeds, disguises the origin of criminal proceeds, or conceals criminal proceeds is subject to imprisonment not exceeding five years or a fine not exceeding KRW 30 million. Article 8 of the POCA provides for the confiscation of criminal proceeds and Article 10 of the same Act provides for the confiscation of property of equivalent value to criminal proceeds.
KoFIU establishes sound financial practice and protects the nation from the proliferation of anti-social serious crimes by preventing Money laundering activity through financial institutions. To effectively handle the cross-border movement of illegal proceed, which stems from abusing foreign transaction liberation measure, KoFIU built FIU Information System in the end of November 2002. The system allows KoFIU to identify and analyze the person involved in money laundering activity through foreign transaction, financial information etc., even without STR from financial institutions. Besides above activities, KoFIU provides consistent training to financial institutions and is committed to international community by actively participating in global network projects.
KoFIU and its AML/CFT Regime
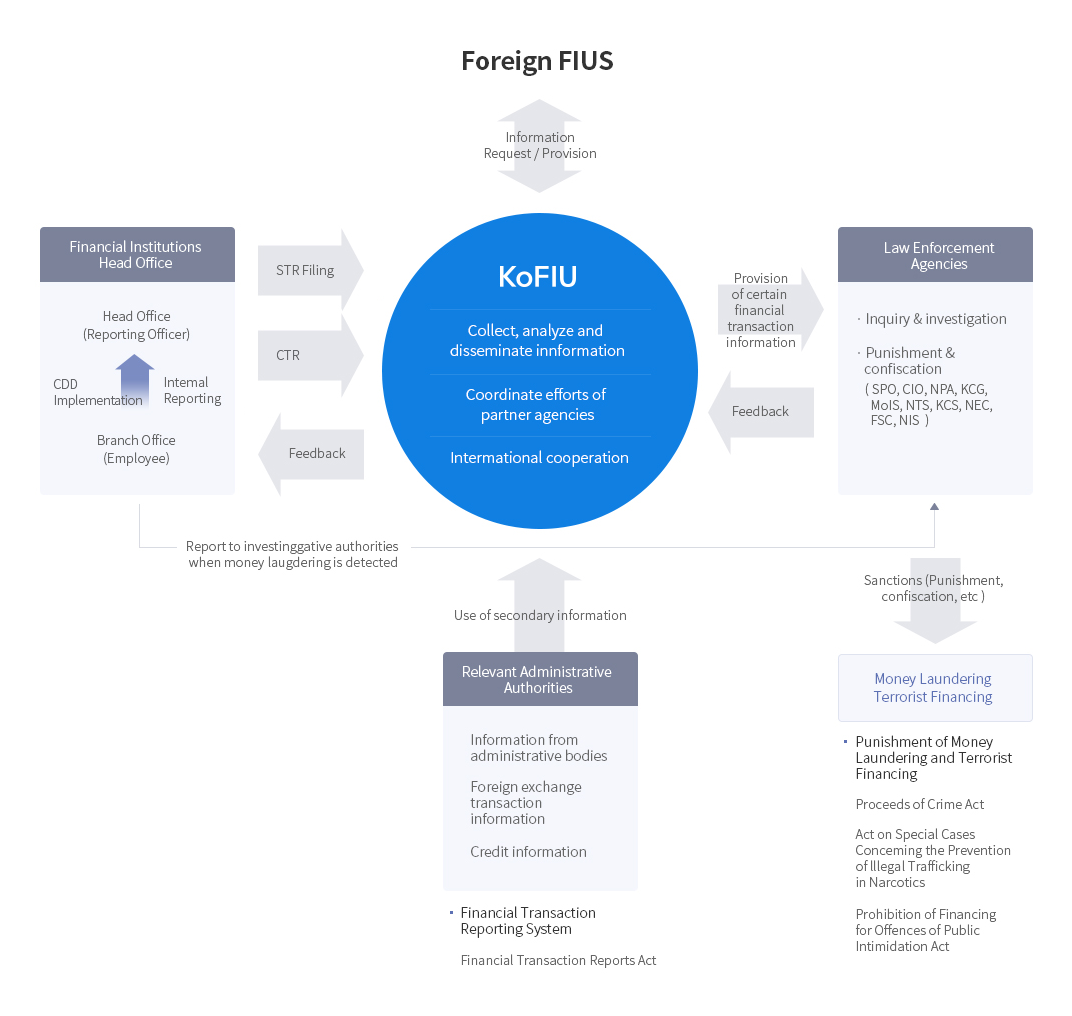
The KoFIU collects and analyzes specific financial transaction data, operates relevant international cooperation, such as information exchange with foreign FIUs, and has set up a system to coordinate with domestic agencies. Reporting entities, such as, financial institutions, file STRs and CTRs to the KoFIU, generally from branch (staff) to the headquarter (reporting officer) through an internal reporting system and CDD implementation. When evidence of a crime is found, reporting entities directly report the case to investigative agencies. Law Enforcement Agencies (Supreme Prosecutors’ Office, National Police Agency, National Tax Service, Korea Coast Guard, Korea Customs Service, Financial Services Commission, National Election Commission, Corruption Investigation Office for High-ranking Officials, Ministry of Interior and Safety, National Intelligence Service) use financial transaction data received from the KoFIU, subsequently, respond with feedback on what was received. Law Enforcement Agencies apply sanctions to severe criminals and money laundering offenders under the AML/CFT regime. Relevant laws include, the Act on Regulation and Punishment, etc. of Criminal Proceeds Concealment, the Act on Special Cases Concerning the Prevention of Illegal Trafficking in Narcotics, and the Act on Prohibitions against the Financing of Terrorism and Proliferation of Weapons of Mass Destruction. The KoFIU, on occasion, uses data from relevant administrative agencies, a centralized credit registry, and a centralized foreign exchange registry. The relevant law is the Financial Transaction Reports Act.